Understanding Kafka: A Message Broker Overview
Message brokers play a critical role in distributed systems by enabling communication between different applications and services. Kafka, a leading distributed event streaming platform, has become a cornerstone for building scalable and fault-tolerant systems.
1. What is Kafka?
Kafka is an open-source distributed event streaming platform designed for high-throughput and low-latency processing. Originally developed by LinkedIn, Kafka is now maintained by the Apache Software Foundation. It enables the storage, processing, and replays of event streams in real time. Key components include:
Producers: Applications or services that send data to Kafka topics.
Consumers: Applications or services that read data from Kafka topics.
Brokers: Kafka servers that store data and serve client requests.
Topics: Categories or feeds to which records are sent and stored.
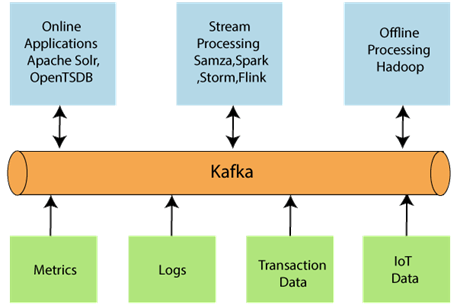
Kafka’s architecture ensures scalability and resilience, making it a preferred choice for modern data pipelines and streaming analytics.
2. Supported Protocols
While Kafka uses its proprietary Kafka Protocol, it also supports integrations with other messaging standards. Common protocols include:
- AMQP (Advanced Message Queuing Protocol): Primarily used by traditional message brokers like RabbitMQ, Kafka connects through connectors for compatibility.
- HTTP/REST: Tools like Kafka REST Proxy enable HTTP-based communication for producing and consuming messages.
- gRPC: Can be integrated for client-server communication in microservices.
These protocols enhance Kafka’s flexibility, allowing seamless interaction with diverse ecosystems.
3. UI Interfaces for Kafka
Several tools provide user-friendly interfaces to manage and monitor Kafka clusters:
- Confluent Control Center: A comprehensive UI for Kafka monitoring and management.
- Kafdrop: A lightweight, open-source web UI for browsing Kafka topics, consumers, and brokers.
- Lens(lenses.io): A developer-friendly interface focused on debugging Kafka streams.
- AKHQ: A modern UI for topic management, consumer group monitoring, and ACL administration.
These interfaces simplify Kafka management tasks for developers and administrators.
4. Implementations in Different Programming Languages
Kafka’s robust client libraries and APIs enable seamless integration across popular programming languages:
- Java: The official Kafka client library (
org.apache.kafka) supports full functionality. - Python: Libraries like
kafka-pythonandconfluent-kafka-pythonare widely used. - C#: The
Confluent.KafkaNuGet package provides a high-performance Kafka client. - Node.js: Libraries like
kafka-nodeandkafkajsenable JavaScript-based applications to integrate with Kafka. - Go:
saramaandconfluent-kafka-goare popular libraries for Go developers.
These libraries support producing, consuming, and managing Kafka messages efficiently.
5. Testing Kafka in QA
Testing Kafka can be challenging due to its asynchronous nature and real-time processing. QA teams can consider the following approaches:
- Unit Tests: Mock Kafka producers/consumers using libraries like
MockKafka(Java) or pytest-kafka (Python). - Integration Tests: Use in-memory Kafka clusters (e.g.,
EmbeddedKafkafor Java) to simulate real scenarios. - Performance Testing: Tools like Apache JMeter and Gatling support Kafka-specific plugins for load testing.
- Consumer Lag Monitoring: Verify that consumers process messages without significant delays using metrics.
QA teams should focus on data consistency, scalability, and latency metrics during testing.
6. Kafka vs. Azure Service Bus
| Feature | Kafka | Azure Service Bus |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Distributed Event Streaming Platform | Cloud-Based Message Broker |
| Protocols | Kafka Protocol, REST, AMQP | AMQP, HTTPS |
| Persistence | Durable by default | Optional, based on queues/topics |
| Scaling | Horizontal scaling with partitions | Auto-scaling in Azure environment |
| Use Case | High-throughput, real-time data streams | Enterprise workflows, hybrid setups |
| Setup | Self-managed or Confluent Cloud | Fully managed by Azure |
| Latency | Sub-millisecond (with tuning) | Typically higher |
7. Footnotes
- Apache Kafka Documentation: Explore Kafka’s official documentation for detailed insights.
- Confluent Kafka: Learn more about managed Kafka solutions at Confluent.io.
- Comparison Details: Azure Service Bus documentation can be found here.
- Kafka Testing Tips: Check out
MockKafkafor Java testing here. - Multimedia book about Kafka (Cartoon story) : https://www.gentlydownthe.stream/
- My personal project for checkin basic Kafka features. Impletentation in Python. GitHub repo: https://github.com/ooge0/kafka-app-demo
- Web post: Apache Kafka Architecture. https://www.javatpoint.com/apache-kafka-architecture
- Deploy Kafka UI tool | Medium
- Fix for issue: Running Kafka on Windows 10 fails: The system cannot find the path specified
- Book: Mastering Kafka Streams and ksqlDB: Building Real-Time Data Systems by Example Mitch Seymour. Read on coursesidekick.com